- Offices Time:24 Hours Online
- Email:[email protected]
- WhatsApp:+8618339938759
Posted on December 1, 2022
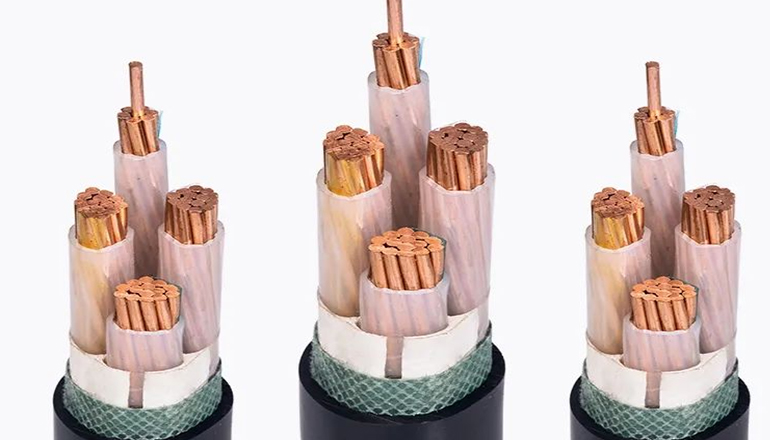
The structure and application of concentric cable
Concentric cables are mainly used in industry and distribution boards, power stations, house connection boxes and street lights for control pulse and test data transmission and control cables. In general, it is mainly used where increased electrical and mechanical protection is required. These cables are mainly installed outdoors, underground, indoors or in cable ducts. Due to the typical structure of the concentric wires, more cable splices can be obtained without cutting any conductors. In this way, operational reliability is guaranteed.
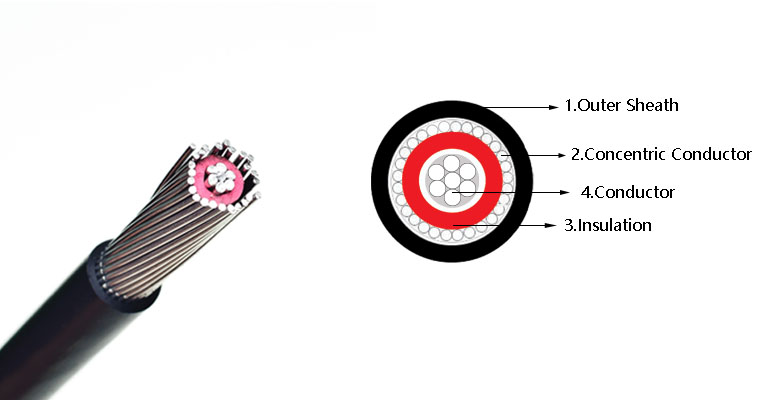
Concentric cable is also called coaxial cable. It is a transmission line used to guide electromagnetic waves. Its structure is generally composed of four layers of materials. There are two conductors in a concentric structure. The two conductors are separated by insulating materials. The outermost Layers are usually wrapped with insulating material as a protective skin.
Coaxial cables can transmit analog and digital signals in a low-loss manner, and are suitable for a variety of applications, including television broadcasting systems, long-distance telephone transmission systems, short-distance jumpers between computer systems, and local area network interconnections. Coaxial cable grew rapidly as a means of distributing television signals to thousands of homes, known as the cable television network. A cable TV system can load dozens or even hundreds of TV channels, and its transmission range can reach tens of kilometers.
1.Detailed structure of concentric cable
(1) Conductor: solid or stranded aluminum conductor or copper conductor
(2) Insulation layer: use XLPE/PE/PVC
(3) Concentric layer: single layer ordinary annealed aluminum wire or copper wire
(4) Sheath: Black PE or PVC

2.What are the characteristics of concentric cables?
(1) High temperature resistance, good aging resistance, good environmental resistance.
(2)Waterproof and corrosion resistant to ensure the safety of product transmission.
(3) Good anti-interferenece ability, stable data transmission.
3.What are the advantages of concentric cables?
The impedance characteristics of the concentric cable are determined by the structure and material of the cable, by the ratio of the inner diameter of the outer conductor to the outer diameter of the inner conductor and the relative permittivity of the dielectric. If the outer diameter of the concentric cable is constant, the diameter of the inner conductor When the diameter of the inner conductor becomes larger, the characteristic impedance will become lower, and the diameter of the inner conductor will become smaller, and the characteristic impedance will become higher. In addition, the characteristic impedance is inversely proportional to the square root of the relative permittivity, so the higher the relative permittivity, the lower the characteristic impedance. Therefore, theoretically, the characteristic impedance of the coaxial cable can have any value according to the free combination of structure and material.
In actual use, it is difficult to manufacture extremely thin inner conductors and extremely thin dielectrics, so the characteristic impedance value range of coaxial cables is limited to changes between several ohms and hundreds of ohms. However, the characteristic impedance of coaxial cables in practical use is almost always 50Ω or 75Ω.
Post categories
Most Popular Posts
-
The 136th Canton Fair welcomes you to participate!
October 12, 2024 -
High temperature cable introduction
July 26, 2024 -
Kenya Power and Energy Exhibition 2024
June 11, 2024 -
Introduction of rubber sheathed cable
June 5, 2024





