- Offices Time:24 Hours Online
- Email:[email protected]
- WhatsApp:+8618339938759
Posted on December 6, 2022
How to choose low-voltage power cables?
In the AC system, the phase-to-phase rated voltage of the conductors of the power cables must not be lower than the working line voltage of the circuit used. Low-voltage power cables should be insulated with XLPE or PVC extruded insulation. In the previous article, we talked about low-voltage For the laying of power cables, today we will introduce how to choose low-voltage power cables!
1.Select according to the environment in which the cable is used and the characteristics of the equipment.
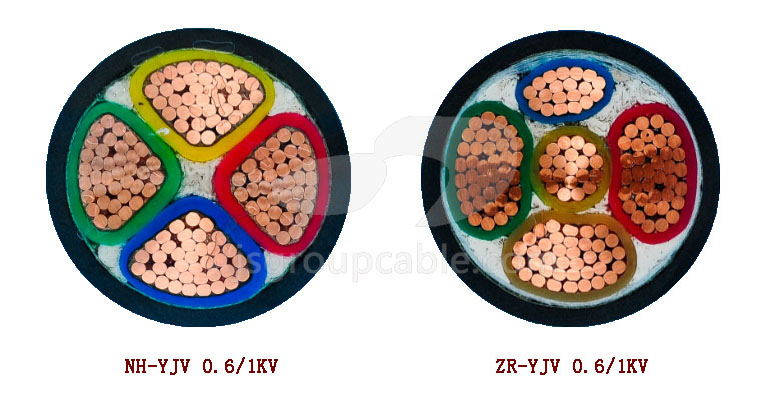
(1) Flame retardant power cable: ZR-YJV-0.6/1kV

(2) Fire-resistant power cable: NH-YJV-0.6/1kV

(3) Rubber-sheathed power cable: YC-450/750V
(4) Flame-retardant rubber-sheathed power cable: ZR-YC-450/750V
2.Selection of cross-section of low-voltage power cables
The cross section of low-voltage power cables can be divided into the following four types according to the selection of technical methods
(1) Temperature rise method
The allowable carrying capacity of the long-term continuous rated load of the cable should not be less than the maximum calculated current value of the electrical load, and it can ensure that its operation is within the allowable temperature rise range. If the cross section is selected small, the allowable carrying capacity is less than the load current, the temperature rise will exceed the allowable value, and the aging of the insulating material will be accelerated, the insulation degree of the wire will be reduced, and the safety of electricity use will be affected. On the contrary, if the cross section of the cable is selected large, the project cost will be increased. , resulting in a waste of material funds. Take the three-phase power equipment that works for a long time, such as water pumps and fans, as an example.
(2) Voltage loss method
When checking the cross-section according to the voltage loss, the terminal voltage of various electrical equipment should meet the requirements for normal operation and startup. Calculate the loss voltage, according to the cross-sectional area of the cable, calculate the result, and select the appropriate cable according to the cross-sectional area of the cable.
The conductor should meet the requirements of dynamic stability and thermal stability. When a short-circuit fault occurs on a low-voltage distribution line, before the protective device operates, the temperature of the conductor will rise sharply due to the thermal effect of the short-circuit current, resulting in damage to the conductor insulation. The laid wires should be sufficient to withstand normal tension and electric power, and should not shrink or break, so as to ensure the safe transmission of electric energy. The mechanical strength is closely related to the laying method of cables, such as laying multiple cables side by side in the air, laying underground directly, laying pipes, laying overhead, laying trunking, laying cable trenches, laying cable tunnels, etc.
Different laying methods will affect the allowable current carrying capacity of the wire. The mechanical damage caused by the turning of the low-voltage power cable should also be worthy of attention. During construction, if the turning angle is too large, the inside of the conductor may be mechanically damaged, and the mechanical damage will cause the insulation degree of the cable to decrease, resulting in failure.
Because, when the cable is turned and reserved, the cable should be naturally bent as much as possible to minimize the torsion of the cable and reduce the phenomenon of internal mechanical damage.
In addition, in engineering practice, it is easy to ignore unfavorable factors such as temperature, water bubbles, interference, corrosion, etc. These factors may lead to hidden accidents or failures.
3.Common line faults of power cables
(1) Short-circuit fault: There are two-phase short-circuit and three-phase short-circuit, mostly caused by hidden dangers left in the manufacturing process.
(2) Grounding fault: A certain core or several cores of the cable break down to the ground. If the insulation resistance is lower than 10kΩ, it is called low resistance grounding, and if it is higher than 10kΩ, it is called high resistance grounding. Mainly due to cable corrosion, lead skin cracks, dry insulation, joint technology and materials.
(3) Broken line fault: a certain core or several cores of the cable are completely or partially broken. Mechanical damage, terrain changes, or short circuits can cause disconnections in cables.
(4) Mixed failure: more than two kinds of failures mentioned above.
4.Power cable line fault solution
(1) External force damage: During the storage, transportation, laying and operation of cables, they may suffer from external force damage, especially the directly buried cables that have been in operation are vulnerable to damage during the ground construction of other projects. Such accidents often account for 50% of cable accidents. In order to avoid such accidents, in addition to strengthening the work quality of cable storage, transportation, laying and other links, it is more important to strictly implement the ground breaking system.
(2) Corrosion of protective layer: Electrochemical corrosion of underground stray current or chemical corrosion of non-neutral soil makes the protective layer invalid and loses the protective effect on insulation. The solution is to install drainage equipment in stray current-intensive areas; when the local soil on the cable line contains chemical substances that damage the lead sheath of the cable, this section of the cable should be installed in the pipe, and the neutral soil should be used as the liner of the cable And cover, but also on the cable with asphalt.
(3) Overvoltage and overload operation: Improper voltage selection of low-voltage power cables, sudden high-voltage intrusion during operation, or long-term overloading may damage the insulation strength of the cable and break down the cable. This needs to be solved in a timely manner by strengthening inspections and improving operating conditions.
(4) Outdoor terminals soaked in water: due to poor construction, the insulating glue was not filled, causing the terminals to soak in water, and finally exploded. Therefore, it is necessary to strictly implement the construction process regulations, carefully check and accept; strengthen inspection and timely maintenance. The oil leakage of the terminal head destroys the sealing structure, causes the impregnating agent at the end of the cable to dry up, increases the thermal resistance, accelerates the aging of the insulation, easily absorbs moisture, and causes thermal breakdown. When oil leakage from the terminal head is found, the inspection should be strengthened, and if it is serious, the power should be cut off and redone.
Post categories
Most Popular Posts
-
The 136th Canton Fair welcomes you to participate!
October 12, 2024 -
High temperature cable introduction
July 26, 2024 -
Kenya Power and Energy Exhibition 2024
June 11, 2024 -
Introduction of rubber sheathed cable
June 5, 2024





